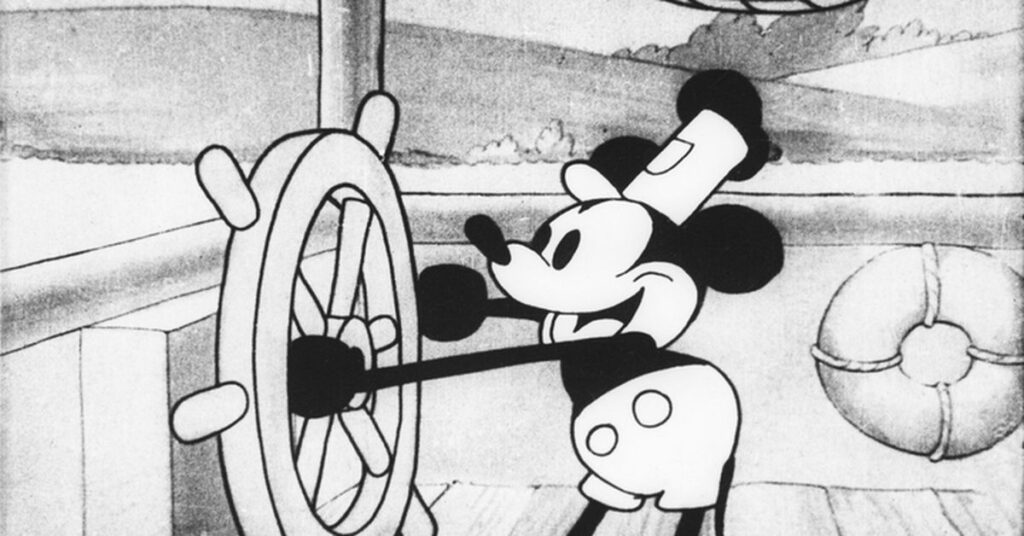
It’s finally happening: Nearly a century later, Mickey Mouse is freed from Disney’s copyright shackles.The first version of this iconic cartoon character appeared in Steamboat Willie and silent version crazy plane, entered the public domain in the United States on January 1, 2024. (Fortunately, early versions of Minnie Mouse are also included.) There are still intricate conservation efforts surrounding Mickey, but today is the moment that public domain advocates have been waiting for decades — and there are plenty of other exciting new entries .
As usual, Duke Law School’s Center for Public Domain Studies has compiled a summary of notable works whose copyright protection has expired in the United States today. The list includes recordings from 1923 as well as works published in other media in 1928. These include:
You can find a large number of public domain recordings available for download at the National Jukebox at the Library of Congress. If you’ve been inspired by the above media or any other works that have entered the public domain this year, technical dirt The sixth annual Public Domain Game Jam will be held to celebrate the games based on them.
Of course, copyright law is especially complicated for an ongoing character like Mickey Mouse. Public domain versions of the character do not include major design changes made in later works, such as Mickey’s Apprentice fantasia 1940.You can’t make a production that falsely describes itself as a Disney production or official merchandise because Mickey Mouse is also Registered trademark of Disney. Jennifer Jenkins, director of Duke University’s Center for Public Sphere Studies, explains the law more fully on Duke’s blog.
The public domain should be the final destination for any copyrighted work—it’s part of the compromise that recognizes the freedom to allow artists and thinkers to control and profit from their works in the short term, while freely building on each other’s ideas in the long term. The good, the balance Disney relies on when crafting fairy tale adaptations snow White and cinderella. (This is also an important factor in allowing archivists to preserve old media after its creator has died or is no longer found, as it allows copying without legal issues – and only for a small proportion of copyrighted works remained commercially valuable throughout the term of protection.) But it was frozen for 20 years in the United States due to the Sonny Bono Copyright Term Extension Act, which was derided as the “Mickey Mouse Protection Act” because of its delays Steamboat Willieof into the public domain. Despite the moniker, Disney wasn’t the only company lobbying for its passage.
As a result, Mickey Mouse became a symbol of expanded copyright protections and (to varying degrees of fairness) Disney’s vested interest in intellectual property law. For example, when Disney criticized Florida’s “Don’t Say Gay” law, which outraged Republican politicians, Sen. Josh Hawley (R-Mo.) proposed in the name of stripping “woke businesses like Disney of their special copyright protections.” A near-nuclear intellectual property law rollback. ”. We’ll likely see legal battles over the precise limits of Mickey in the public domain, just as we do with other characters like Sherlock Holmes – but today, it’s a good day to think about new uses for old media.