Vietnamese electric vehicle manufacturer VinFast plans to invest an initial US$500 million to set up a comprehensive factory in India to enter the world’s third largest automobile market.
The company said the memorandum of understanding with the Tamil Nadu government announced on Saturday earmarked investments of up to $2 billion, but gave no specific timeline.
Construction of the Thoothukudi plant is scheduled to begin this year, with an annual production capacity of up to 150,000 vehicles. It is expected to create 3,000-35,000 jobs.
The southern Indian state is a major automobile manufacturing hub, hosting production facilities of well-known companies such as BMW, Hyundai and Renault-Nissan, as well as electric vehicle manufacturers such as China’s BYD, India’s Ather Energy and Ola Electric. Two wheelers. (Ola Electric plans to launch in Mumbai this year.)
“We are delighted that VinFast has chosen to invest in Tamil Nadu to establish its integrated electric vehicle factory. With strong capabilities and an unwavering commitment to a sustainable future, we I am confident that VinFast will be a reliable economic partner and important contributor to the long-term development of Tamil Nadu,” Nadu, in a statement.
Apart from the manufacturing facility, the automaker is also looking to develop a pan-India dealership network to cater to the needs of consumers in the world’s third-largest four-wheeler market.
“This MoU reflects VinFast’s strong commitment to sustainability and its vision for a zero-emission transportation future. We believe that investing in Tamil Nadu will not only bring significant economic benefits to both parties, but will also help accelerate India’s green energy transition in the region,” said Tran Mai Hoa, Vice CEO of Sales and Marketing at VinFast Global.
Founded in 2017, VinFast has been producing electric vehicles since 2021 and sells them to markets such as the United States and Canada in addition to the domestic market in Vietnam. The loss-making company, often compared to Tesla, listed on Nasdaq in August through a SPAC deal with Black Spade and announced plans to enter India in October.
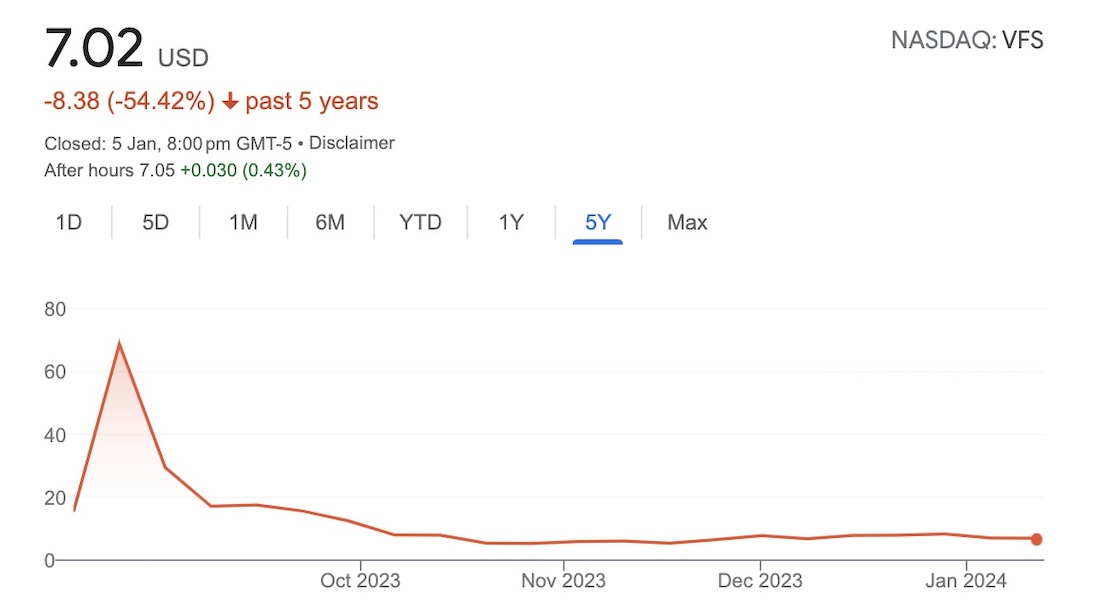
Although VinFast hopes to expand its market by investing in India, the company faces financial challenges in the existing market. The company cut jobs in the U.S. and Canada last year and faced criticism over quality and safety issues with its VF8 EV. Since its IPO, VinFast shares have fallen more than 81% to $7.02.
Nonetheless, India has been an attractive market for global EV manufacturers as the country aims to achieve 30% electrification by 2030. Homegrown automaker Tata Motors has so far been the dominant maker of electric vehicles in the country, while Chinese players BYD and MG Motor are looking to expand their presence in the country with electric models. Similarly, South Korea’s Hyundai Motor has started introducing its electric vehicles into the Indian market to meet the growing demand. Tesla has also made aggressive efforts to enter the market, setting up a factory in the western state of Gujarat.
According to data on the government’s Vahan portal, the current penetration rate of electric vehicles in the Indian market is only 0.25% of the total car sales of more than 51 million units. However, the government provides incentives and subsidies to develop the electric vehicle market.
The India deal was announced earlier on Saturday after VinFast named its founder and biggest backer Pham Nhat Voung as chief executive.

3 Comments
Pingback: Vietnamese electric car maker VinFast plans to invest $2 billion in India – Tech Empire Solutions
Pingback: Vietnamese electric car maker VinFast plans to invest $2 billion in India – Mary Ashley
Pingback: Vietnamese electric car maker VinFast plans to invest $2 billion in India – Paxton Willson