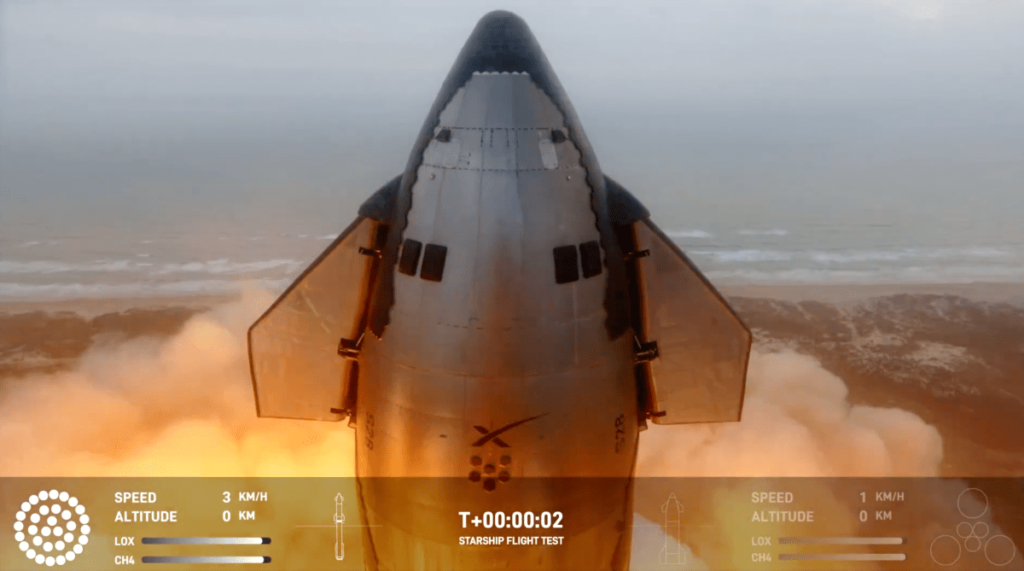
SpaceX is continuing to make progress on the development of Starship, the largest rocket ever built, with Thursday’s third test flight completing far more than the previous two tests.
The 400-foot-tall Starship rocket lifted off from SpaceX’s Starbase facility in southeast Texas at 8:25 a.m. local time. Although SpaceX has been developing Starship for years, this is only the company’s third attempt at an orbital mission.
After liftoff, the starship made a nominal—normal ascent in aerospace—ascent. All 33 Raptor engines on the Super Heavy booster were operating as designed, with two-stage separation taking approximately 2 minutes and 45 seconds after the mission began. Crucially, the launch vehicle uses a new stage separation technology called “thermal staging,” in which the upper stage (also known as a starship) fires its engines to push away the super-heavy booster. Thermal classification technology was used for the first time during the second Starship test flight last November.
From there, the starship’s upper levels continue to ascend into orbit. SpaceX CEO Elon Musk congratulated the X team, saying, “Starship has reached orbital speed!”
Starship reaches orbital speed!
congratulations @SpaceX team! !
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 14, 2024
The booster performed what’s called a boost burn to adjust its trajectory as it aimed for splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico – the same maneuver Falcon 9’s booster performed to land vertically on Earth – but its engines didn’t Can be re-ignited during the landing burn phase. The Super Heavy subsequently disappeared.
The company has hit another new milestone after opening Starship’s payload door for the first time. This capability is critical to SpaceX’s plan to quickly deploy hundreds of next-generation Starlink satellites. Another demonstration, a propellant transfer demonstration, was also completed, but the company did not disclose the results of that test.
Propellant transfer is an important part of the company’s plans for NASA to return humans to the moon. As part of SpaceX’s plan to carry out NASA missions, the company has determined the mission architecture, which may include more than a dozen Starship refueling trips.
Being able to refuel vehicles will also be necessary for future missions to Mars.
The Starship continued to coast, but about half an hour later, the company said it would not attempt to reignite the engines to continue testing. SpaceX did not elaborate on why it decided not to continue the live broadcast.
Instead, they let gravity do its thing, with Earth’s powerful pull pulling the starship back into the lower atmosphere.Ultimately, mission controllers were unable to re-establish communications with the starship, resulting in Dan Huot of SpaceX announced that they had lost the ship: “There was no splashdown today, but it’s incredible to see again how far we’ve come this time,” he said.