Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a number of GitHub repositories offering cracking software used to spread an information-stealing program called RisePro.
The event is codenamed githubAccording to G DATA, 17 repositories related to 11 different accounts are included. The relevant repository has since been deleted by a Microsoft subsidiary.
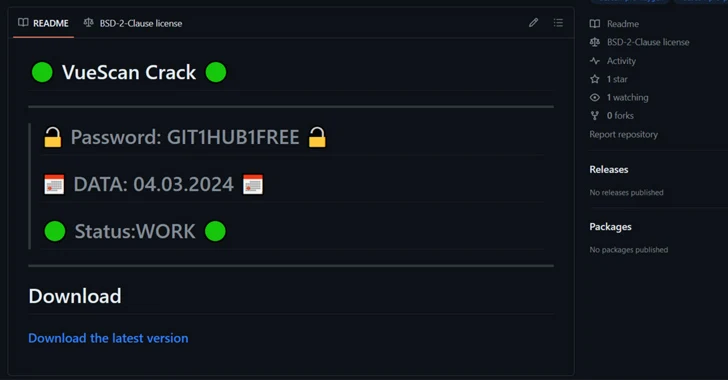
“The repositories look similar, have a README.md file and promise to provide free cracking software,” the German cybersecurity company said.
“Green and red circles are commonly used on Github to display the status of automated builds. The Gitgub threat actors added four green Unicode circles to their README.md, pretending to display status next to the current date and providing legitimacy and recency a feeling of. “

The repository list is as follows, each repository points to a download link (“digitalxnetwork[.]com”) contains RAR archives –
- andreastanaj/AVAST
- andreastanaj/voice booster
- aymenkort1990/fabfilter
- BenWebsite/-IObit-Smart-Defrag-Cracked
- Faharnaqvi/VueScan-Cracked
- javisolis123/Voicemod
- lolusuary/Aomei Backup
- lolusuary/daemon tools
- lolusuary/EaseUS-Partition Master
- lolusuary/SOOTHE-2
- mostofakamaljoy/ccleaner
- rik0v/ManyCam
- Roccinhu/Tenorshare-Reiboot
- Roccinhu/Tenorshare-iCareFone
- True-Oblivion/Aomei-Partition Assistant
- vaibhavshiledar/droidkit
- vaibhavshiledar/TOON-BOOM-HARMONY
The RAR file asks the victim to provide the password mentioned in the repository’s README.md file, which contains an installer file that unpacks the next stage of the payload, an executable file that bloats to 699 MB and is designed to Crash analysis tools such as IDA Professional.
The actual contents of the file (which totals only 3.43 MB) act as a loader, injecting RisePro (version 1.6) into AppLaunch.exe or RegAsm.exe.
RisePro burst into the spotlight in late 2022 when it was distributed using a pay-per-install (PPI) malware download service called PrivateLoader.

Written in C++, it is designed to collect sensitive information from compromised hosts and infiltrate it into two Telegram channels, which are often used by threat actors to extract victims’ data. Interestingly, recent research from Checkmarx shows that it is possible to penetrate an attacker’s bot and forward messages to another Telegram account.
Splunk detailed the strategies and techniques used by Snake Keylogger, describing it as a stealth malware that “employs a multifaceted approach to exfiltrate data.”
“The use of FTP facilitates the secure transfer of files, while SMTP enables the sending of emails containing sensitive information,” Splunk said. “In addition, integration with Telegram provides an instant messaging platform that allows for the immediate transfer of stolen data.”
Stealer malware is becoming increasingly popular, often serving as a primary vector for ransomware and other high-impact data breaches. According to a report released this week by Specops, RedLine, Vidar, and Raccoon have become the most widely used stealers, with RedLine alone stealing more than 170.3 million passwords in the past six months.
Flashpoint noted in January 2024: “The current rise of information-stealing malware is a stark reminder that digital threats are constantly evolving. While the motivations behind their use are almost always rooted in financial gain, stealers are constantly adapting and becoming more sophisticated. Easy to get and use.” Easier to use. “